10 Largest Organs In Human Body
Human body consists of 70 organs that are highly specialized in performing different functions. Millions of cells form part of a...
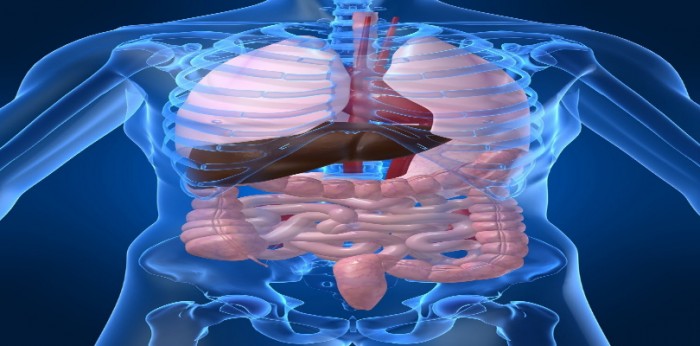
Human body consists of 70 organs that are highly specialized in performing different functions. Millions of cells form part of a single organ. They work together in order to perform functions of the body. Every action taking place inside your body is a result of some organs bringing millions of cells together to achieve a common goal. Complex activities that work towards saving life consume a lot of energy and produce more cells to avoid the total body shut down. Keeping these bodily functions in mind, let’s know about the 10 largest organs in human body.
10. Prostate
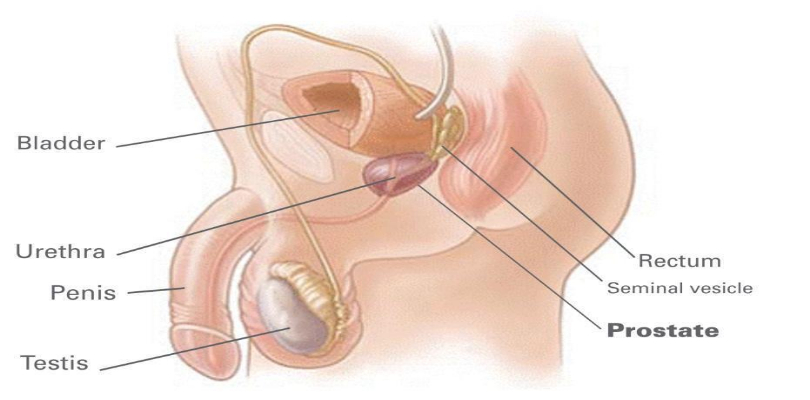
imgsource= “prostatehealthuk”
Prostate is an exocrine gland of the male reproductive system. It differs among species with different anatomy, chemicals and physiology. The average weight of prostate is 20 grams. It is located between the bladder and penis. Prostate secretes a slightly alkaline fluid which is milky or white in appearance. This helps in the protection and nourishment of sperms.
According to a study, the volume of the prostate is significantly related to height and weight in patients with negative biopsy. So, it becomes an important factor in controlling weight. Urethra present below the urinary bladder is surrounded by the prostate and it can be felt during a rectal exam.
9. Thyroid
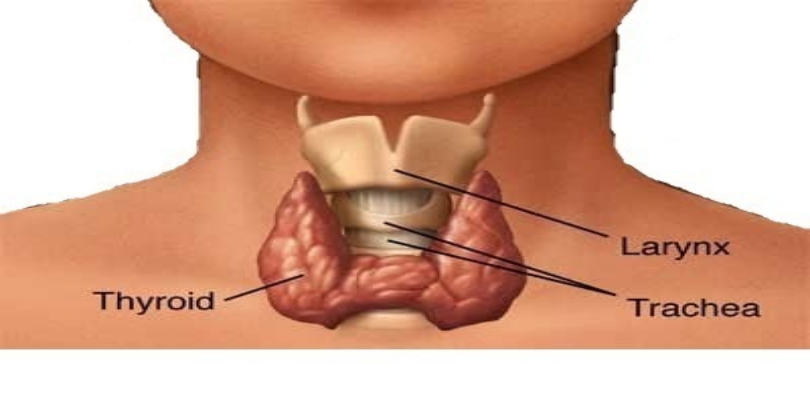
imgsource= “savemoney”
The Thyroid is the largest gland in the human body. It weighs 35 grams. The endocrine gland is a butterfly shaped organ present inside the neck on the front side, below the Adam’s apple. It consists of two lobes left and right and a narrow connecting thyroid isthmus. The gland secretes thyroid hormones namely, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) which influence the protein synthesis and metabolic rate of the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The gland is normally larger in size in women than in men and its size increases during pregnancy.
8. Pancreas
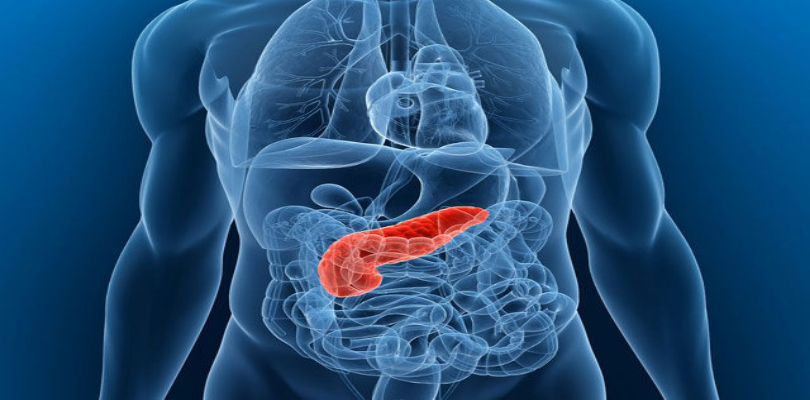
imgsource= “livescience”
The Pancreas is a glandular organ which is a part of the digestive system and the endocrine system of vertebrates. It weighs 95 grams. In the human body, it is situated behind the stomach in the abdominal cavity. Pancreas produces several hormones that circulate in the blood. These are very important for proper functioning of the human body. These include insulin, glucagon, pancreatic polypeptide and somatostatin.
The digestive functions of the pancreas include secretion of pancreatic juices that contain various digestive enzymes helpful in the process of digestion and absorption of nutrients. These enzymes also help in the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids in the chyme (semi fluid mass of partly digested food expelled by the stomach into the duodenum).
7. Spleen
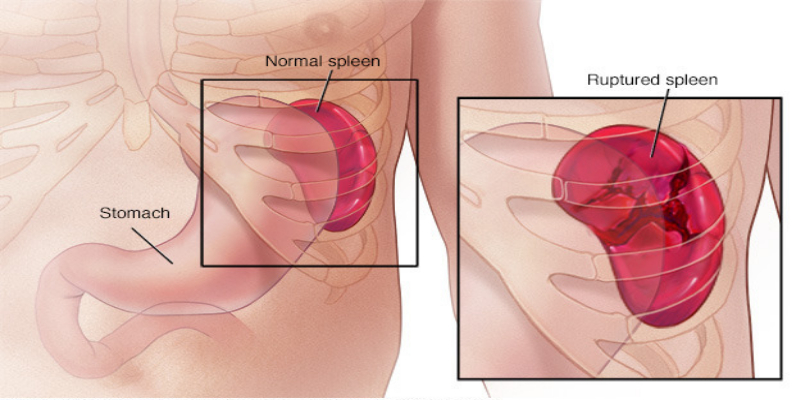
imgsource= “mayoclinic”
The Spleen is a brown colored organ located upper left quadrant of the abdomen. It measures equal to the size of a human fist and weighs around 170 grams. It resembles to the structure of a large lymph node. Spleen primarily acts as a blood filter. With the production of red and white blood cell pulp, spleen ensures the course of enough blood and body fluids through your veins. Spleen contributes significantly towards the immune system. It is a strong defense system against infections. It also works towards lowering the susceptibility of disease causing agents.
6. Kidney
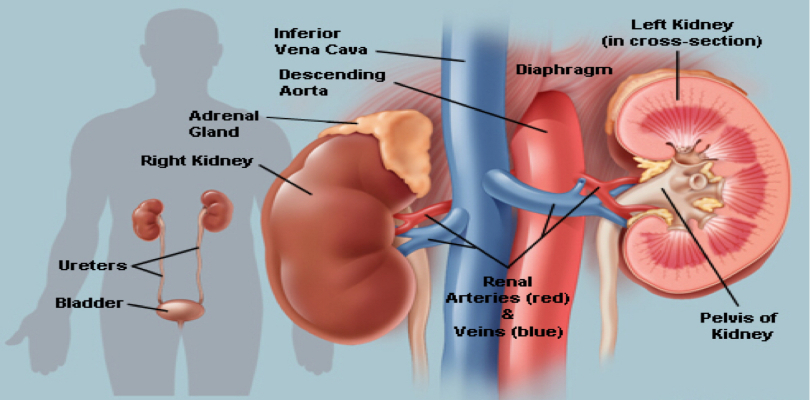
imgsource= “rackcdn”
Kidneys are bean shaped organs that play essential regulatory roles in the human body. There are 2 kidneys in every human being and they weigh about 290 grams. They are located at the rear of the abdominal cavity in the retroperitoneal space. The main function of kidneys is to regulate the balance of electrolytes in the blood. They remove the waste products from the blood by regulating water fluid levels.
Each kidney excretes urine into a ureter which further empties to the bladder. The most amazing fact about kidneys is that they work in the most telepathic way. If anyone gives up, then, another one enlarges to adapt to the duties of both. They purify our blood and cleans for a minimum 50 times in a day.
5. Heart
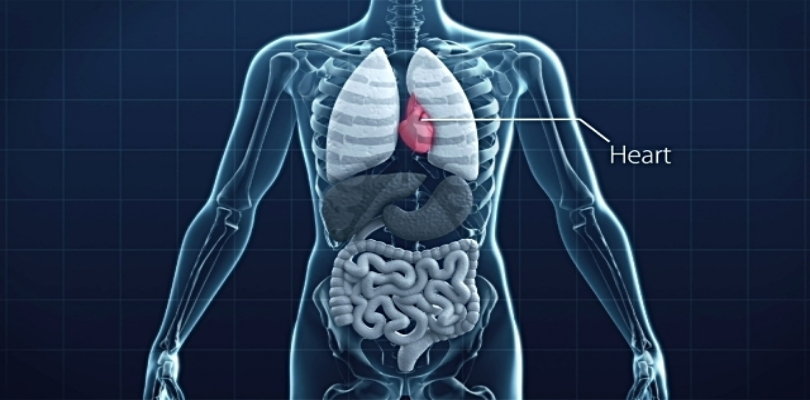
imgsource= “gettyimages”
Nothing can exist without a heart. It is the most essential organ in living beings. Male heart weighs around 315 grams while in females the weight is 265 grams. Located in the middle of the chest, heart pumps blood to all body parts through blood vessels of the circulatory system.
Blood provides oxygen and nutrients to the body. It also assists in the removal of metabolic wastes. This process runs in continuation since our presence in the womb till the day we die. Heart is divided into four chambers – upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles.
4. Lungs
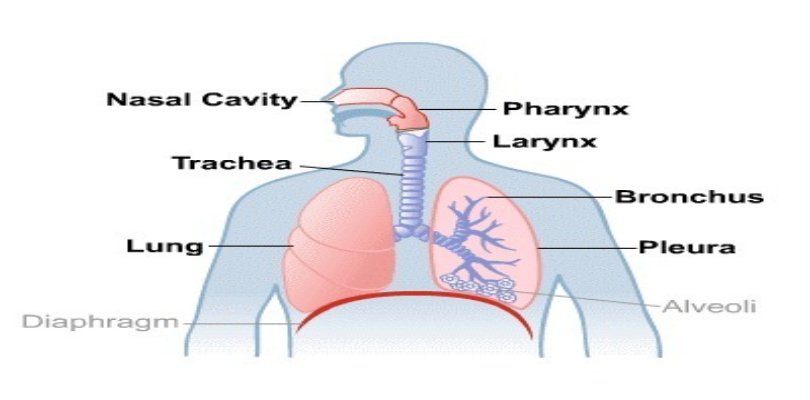
imgsource= “medlineplus”
Lungs are primary organs of respiration in humans and other animals. They are located near the backbone on either sides of the heart. The internal surface area spans the length of 90 meters. Weighing 1,090 grams, lungs can hold up to 5 liters of air. In the process of gas exchange in the respiratory system, lungs extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it to the bloodstream, and releasing the carbon dioxide from blood to the atmosphere. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds possible.
3. Brain
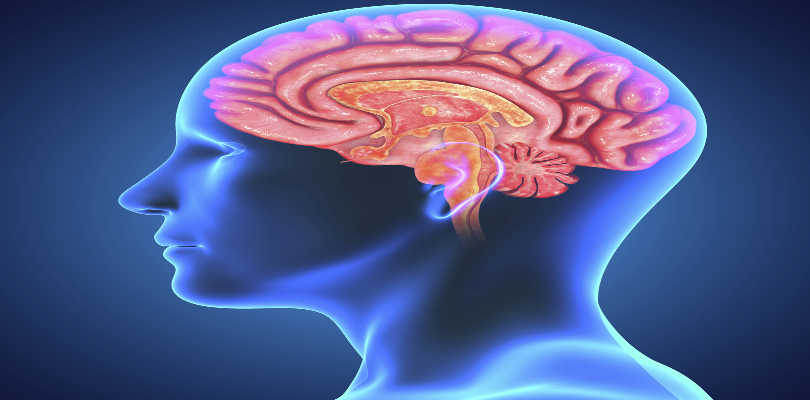
imgsource= “lehacker”
Similar to the heart, brain plays an essential part in the process of existence. A regular brain weighs 1,263 grams. It is protected by the skull in the head. Every action taken by the human body is coordinated by brain. It governs the whole process that brings together the activities of more than 100 billion brain cells. These 100 billion brain cells enable 100 trillion nerve connections with nerve cells for messaging. Brain is designed in such a way that it is connected with every nerve cell throughout the body.
2. Liver
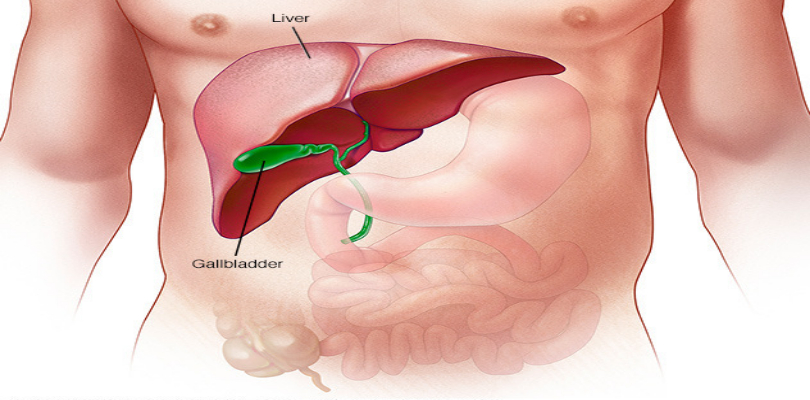
imgsource= “mayoclinic”
Liver is the second largest human organ. Its average weight is 1,560 grams. Situated in the upper right quadrant of abdomen and below the diaphragm, liver performs many functions including metabolites detoxification, production of biochemicals necessary for digestion and protein synthesis. It receives blood that is rich in processed food, stores some of them and distributes rest to different body parts. Whatever remains forms urine and is expelled from the body as waste. Liver is also an accessory bile digestive gland that produces bile. Bile is an alkaline compound that emulsifies lipids thereby assisting digestion.
1.Skin
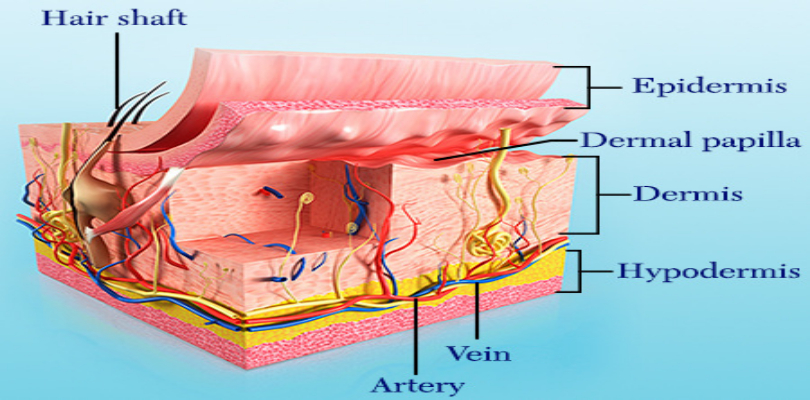
imgsource= “buzzle”
Skin is the largest organ present human body which weighs around 10,886 grams. From top of the head to the soles of feet, skin tissues are attached to every external part of the human body. Skin consists of millions of cells and it is the most exterior form of defense against external forces. Skin is also responsible for the functions of excretion and homeostasis. Other functions performed by skin include sensation, insulation, temperature regulation and production of Vitamin D folates. Skin thickness varies at different locations on body. For example, the skin under eyes is the thinnest (0.5 mm), it is the first area to show signs of ageing. Palm and feet sole skin is 4 mm thick and our back has the thickest skin (14mm) on the body.
Popular Posts
12 Unseen Pictures of Sofia Vergara That are too Hot To Handle
An actress, comedian, producer, television host Sofia Vergara is one of the most loved personality in the TV industry. Bo...
Chandan Roy
Top 10+ McDonald's Characters That Are Better Alternative To The Creepy Clown
When you visit McDonald's, you are entertained by several McD characters designed for kids. Do you know how many Mc D characters are there in total? Let's find it out.
Aaditya M
Top 10 Kidnapping Stories From India That Won The News
The recent reports of crime suggest that it has become an inseparable part of our society and the growing numbers continue to s...
Swati Bhandari








