10 Mind Blowing Facts About Jupiter's Great Red Spot
Do you know that Jupiter is twice as big as other planes in the solar system combined? The great red spot in the Jupiter is the most noticeable feature on the planet, let’s know more about it.
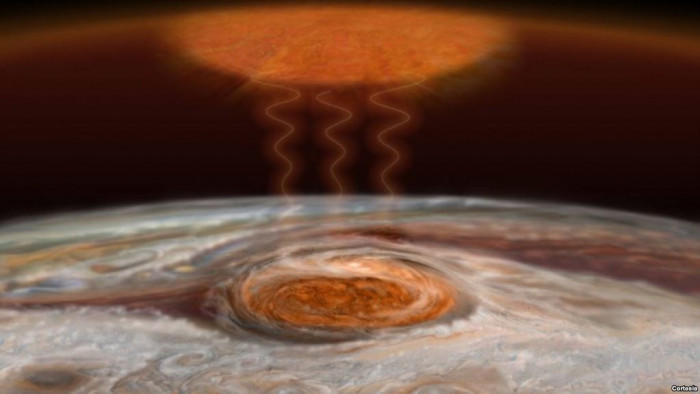
It is no surprise that space is filled with strange activities. Do you know that the most powerful hurricanes ever noticed on earth 1000 miles across with winds blown around 200 mph?
It was quite wide enough to expand across the USA, but some kind of storm is overlooked by the red spot present in the biggest planet Jupiter. This Great red spot has been swirling over the planet for the past 200 years or more, while people saw this spot after the evolution of telescopes in 1600, it is still not clear if it's a different storm or what. Let’s know more facts about Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. (14.1)
Lesser Known Facts About Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
1. The Great Red Spot Wind Speed
This giant great red spot is almost like a hurricane, except the storm ranges with a speed from 270 to 425 mph. This spot is also an anticyclone that means the winds circulate counterclockwise to that of a cyclone on earth. Nearly just like the size of earth, the red spot could bear the terrestrial hurricane.
2. Size of Red Spot is Not Getting Bigger

The giant red spot in Jupiter is not getting bigger, but shrinking in size. The size of the great red spot in 1979 was quite big since then it has nearly reduced 1/3rd in size. At this rate of collapse, it could transform from the oval shape into a circle by the end of 2040. (14.2)
3. It’s still not Clear Why it is Red
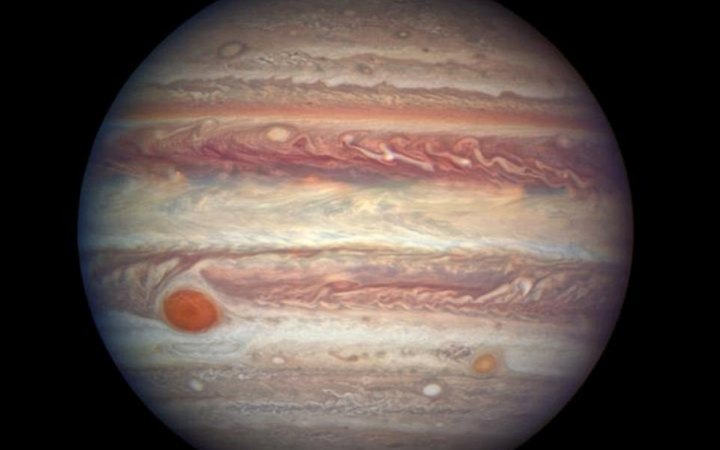

The reason why it is called as Jupiter Great Red spot is still not clear, but it assumed that Jupiter is red because of ammonia filled clouds, a concentration of hydrocarbon acetylene, beating from high powered solar radiation. The chemicals involved might contain a proportion of sulphur and phosphorous which can cause red color.
4. It Moves Across the Planet
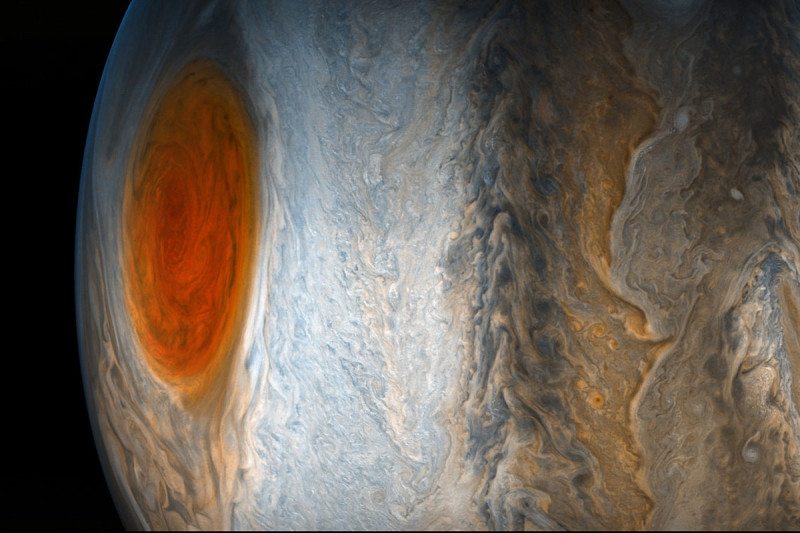

One of the lesser known fact about the Jupiter Great Red Spot is, it moves across the planet but remains at the same distance from the equator. It moves east and west across the planet and the storm persistently prevent it from moving north and south. It locks the anticyclone around 20 degree below the planet's equator. It makes sure that the storm doesn’t enter the northern hemisphere and always remain an anticyclone.
5. It is Shrinking in Size but the Storm is one and Half Times the Size of Earth
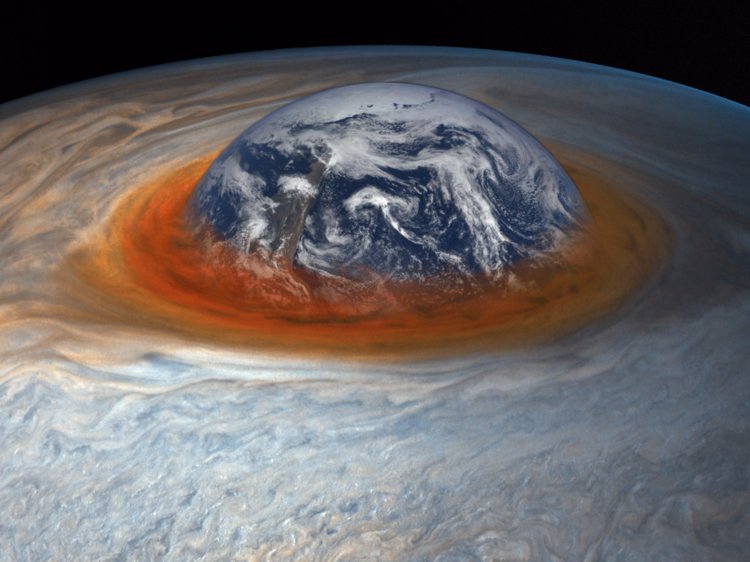
As said The Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is shrinking in size, when measured in 1979 its size was still wide enough to cover 1.3 Earths.
6. It takes 6 Days for Jupiter Red Spot to Make a Full Rotation
While the wind blows at a hundred of miles per hour, the Jupiter Great Red Spot takes nearly 6 days to complete one rotation around Earth. Its encompassing streams tug the storm at different speeds.
7. It is Cold Spot
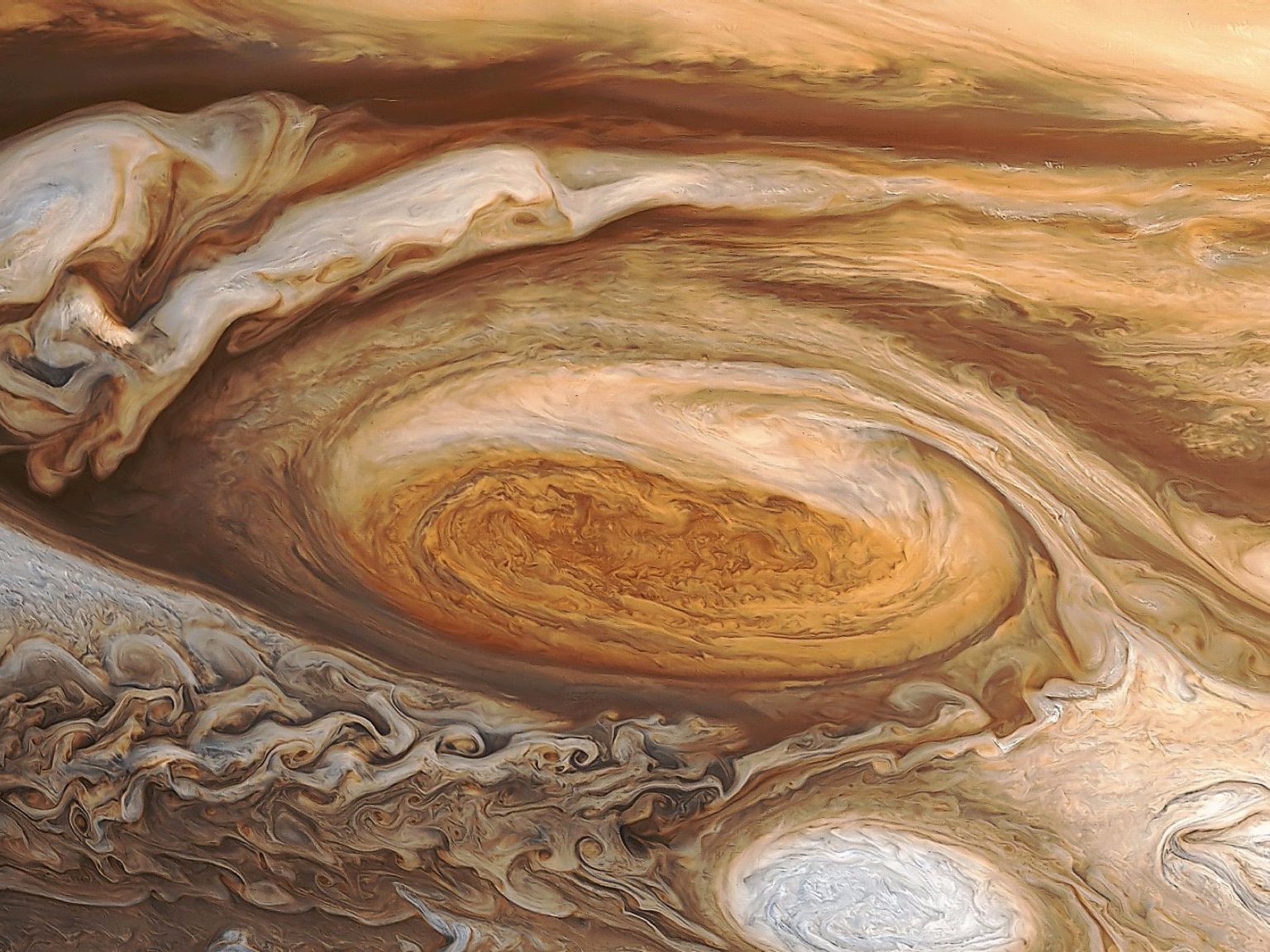

While you were thinking that Great Red Spot is hotter than planets, it remains cold because air rising within the vortex expands and cools down. And the cooling causes the gases to create a thick cloud over the spot.
8. It is considered as the Largest Storms in the System

The Jupiter’s GRS is referred as the largest storms in the solar system. The astronomers use high powered probes like the Hubble space telescope and other to catch the good look of the storm, it can be tricky though. But it can be seen from the Earth every other day for few hours in the evening hours.
9. It has Lapped the Earth 10 Times since Discovery
The GRS is continuously moving across the planet’s atmosphere with varying speed. It is also recorded that the Great Red Spot has lapped the planet at least 10 times since its discovery.
10. It is wedged Between two Jupiter’s High Speed Jet Stream

The roaring GRS sits between the two high speed jet streams. The stream where it sits moves in opposite direction pushing the storm eastward to south and westward towards the north. The flow provides momentum to the anticyclone.
Popular Posts
What Is Trypophobia – A Disgust More Than Fear
"I can't really face small, irregularly or asymmetrically placed holes, they make me like, throw up in my mouth, cry a little bi...
Chandan Roy
16 Interesting Facts About Ambidextrous People
A lefty or left-handed uses his left hand more naturally and dominantly than the right hand. And the righty or right-handed is o...
Ethan Stephans
20 Interesting Facts About Meteoroid, Meteor and Meteorite
Watching celestial objects is a true delight. It is still fun to catch a sight of shooting stars when we grow up. A second of th...
Swati Bhandari








