12 Biggest Nuclear Detonations Ever Recorded in History
A nuclear detonation can cause third-degree burns and huge destruction several miles away. USSR and the US have carried out some of the world’s largest nuclear tests.

There’s no other force more powerful and catastrophic than that of a nuclear detonation. The very first nuclear test took place on 15 July 1945. More than 2,050 nuclear weapons tests have been conducted all over the world. And post the first nuclear test, these weapons became more powerful and explosive after subsequent tests.
With a yield of 20 kilotons, the first nuclear test done in 1945 had an explosive force of 20K tons of TNT. And in all these years, nuclear weapons with yields greater than 10 megatons (or 10 million tons TNT) have been put to test by the US and USSR, countries with lethal nuclear weapons. When pitted against the first atomic bomb, these nuclear weapons proved to be at least 500 times more powerful.
So here are the 12 largest nuclear detonations ever recorded in the past that could have caused major third-degree burns, numerous mortalities, and massive destruction.
Tsar Bomba
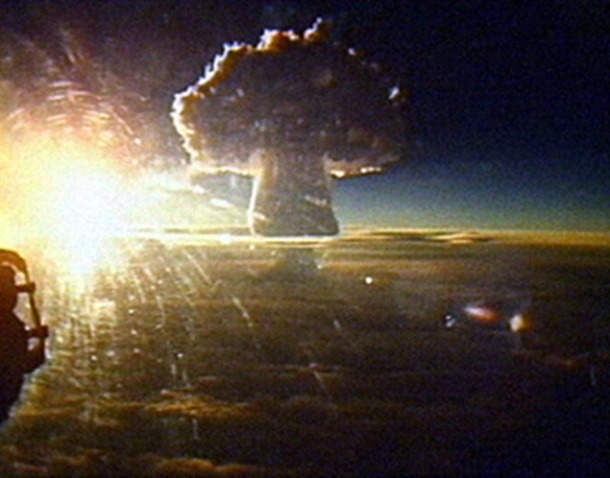

The most powerful nuclear weapon ever tested and detonated, Tsar Bomba had a yield of about 50-58 megatons with the size that’s twice of a second-largest nuclear explosion. Detonated by USSR on 30 October 1961, it is known to have created the largest-ever man-made blast.
According to Slate, this immensely powerful explosion was 3,000 times more powerful than the atom bomb dropped on Hiroshima. It could break windows as far as 560 miles and its flash of light was seen up to 620 miles away.
And do you know that Operation Fishbowl Starfish Prime is the largest man-made nuclear explosion in outer space?
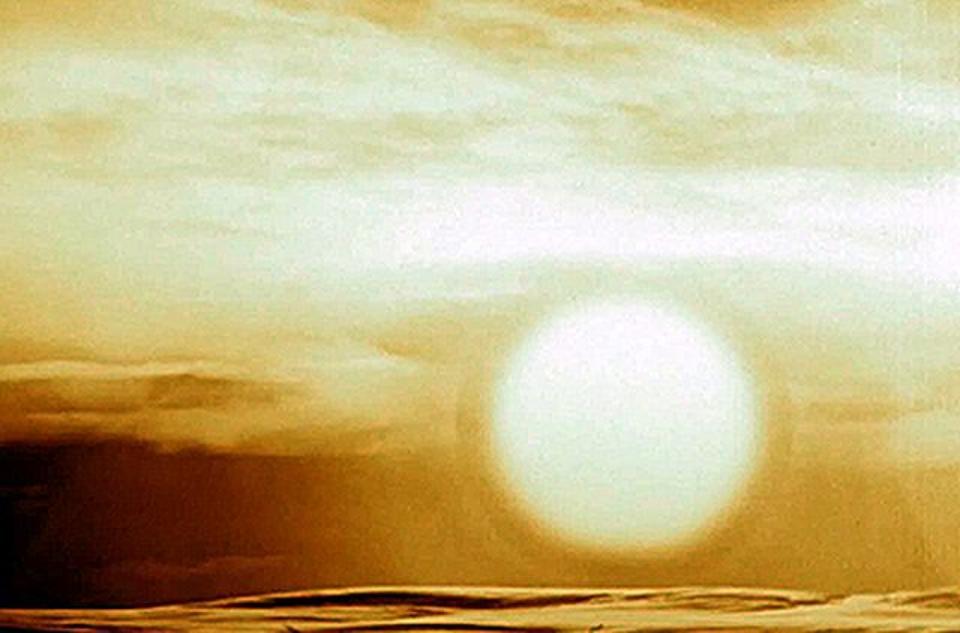

With an atomic bomb of this size, a huge fireball of 6.4 square miles could be created that would have the ability to give humans third-degree burns within 4,080 square miles of the bomb's epicenter.
Ivy Mike
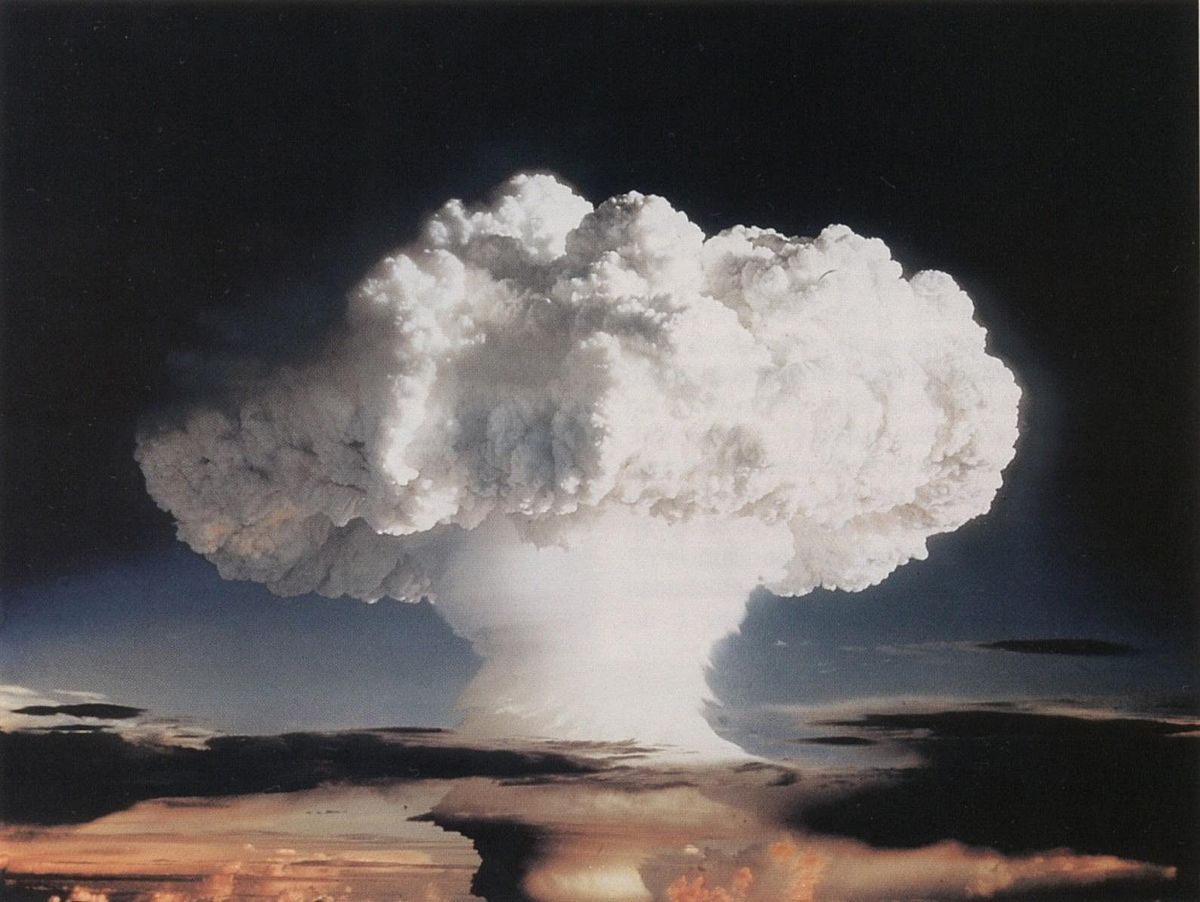

The United States tested Ivy Mike on the Marshall Islands on 1 November 1952. It was the world’s first-ever hydrogen bomb with 10.4 megatons yield, making it 700 times as powerful as the first atomic bomb.
The detonation of this nuclear bomb was so immensely powerful that it vaporized the Elugelab Island (its place of detonation) and left a 164-foot-deep crater. The mushroom cloud of the explosion transmitted to 30 miles in the air.
Castle Bravo
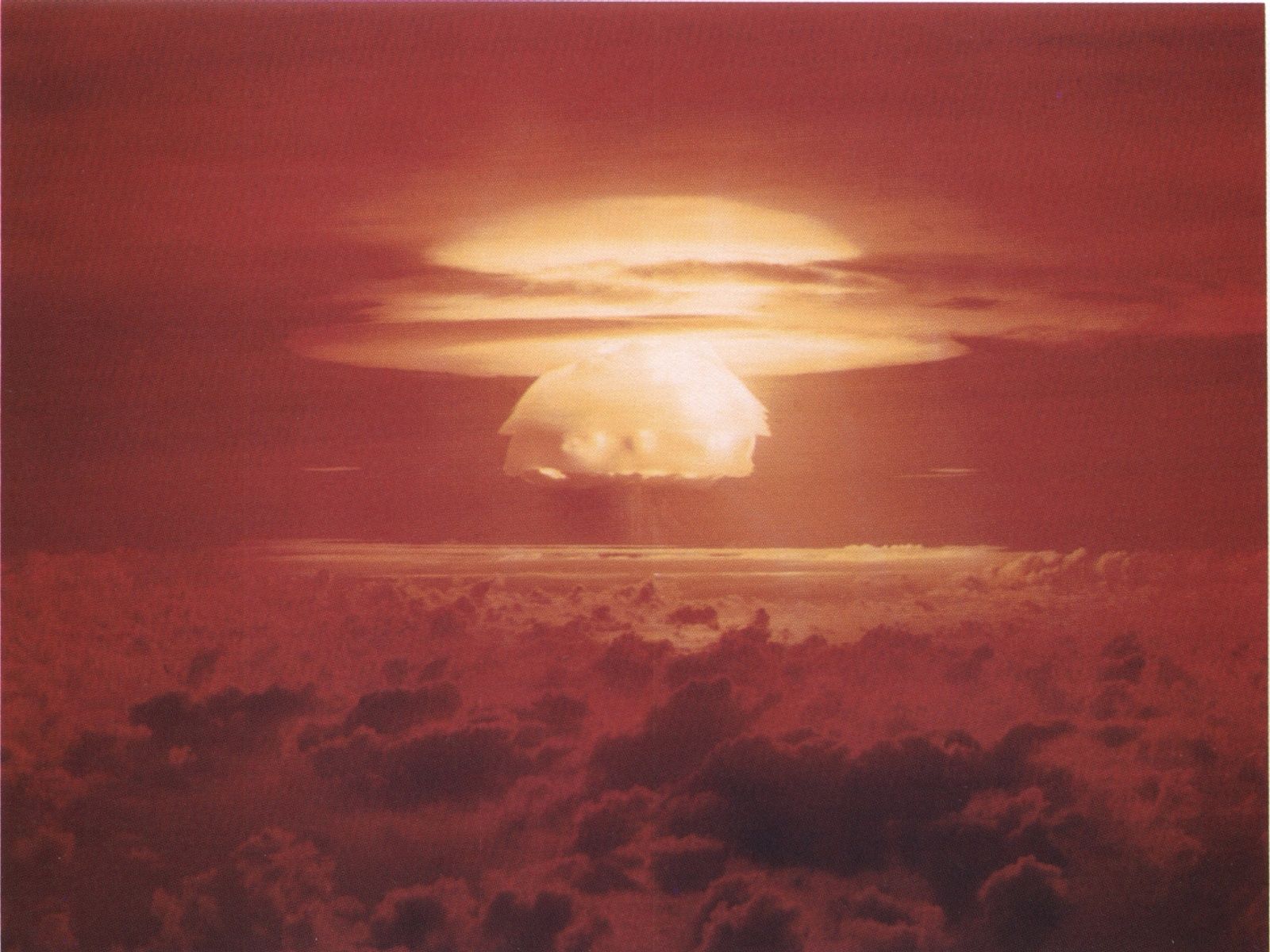

Detonated on 28 Feb 1954, Castle Bravo is the first test of the Operation Castle series, recording the largest-ever US nuclear explosion. Producing a 15-megaton fission blast rather than the anticipated 6-megaton, the mushroom cloud traveled 114K feet into the atmosphere.
Such terrible miscalculation of the US military led to the irradiation of nearly 665 Marshall Islands natives. Also, its deadly radiations claimed the life of a Japanese fisherman who was 80 miles far from the site of detonation. They were 1,200 times powerful than the atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima & Nagasaki during WWII.
Castle Yankee
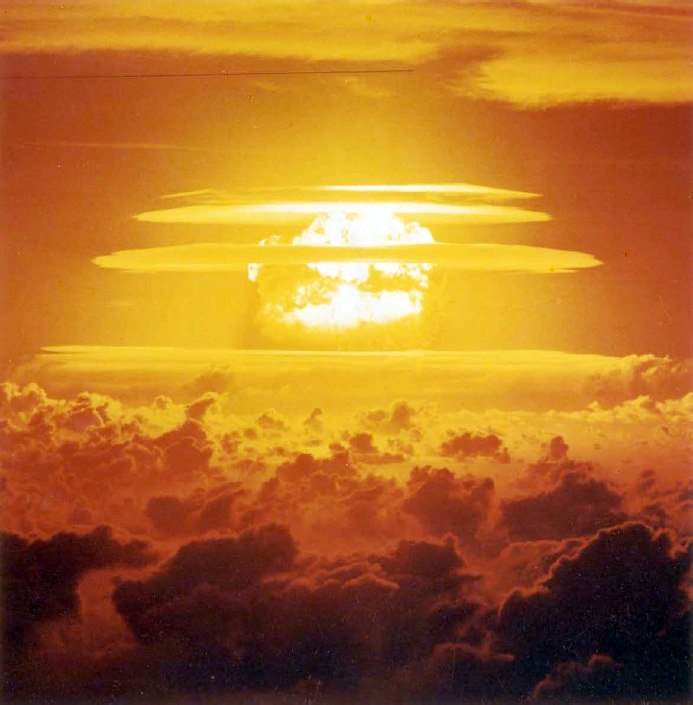

The second most powerful test of the Operation Castle series was Castle Yankee that was carried out on 4 May 1954. A yield of 13.5 megatons, its fallout traveled to Mexico city to far as 7,100 miles four days later.
Castle Romeo
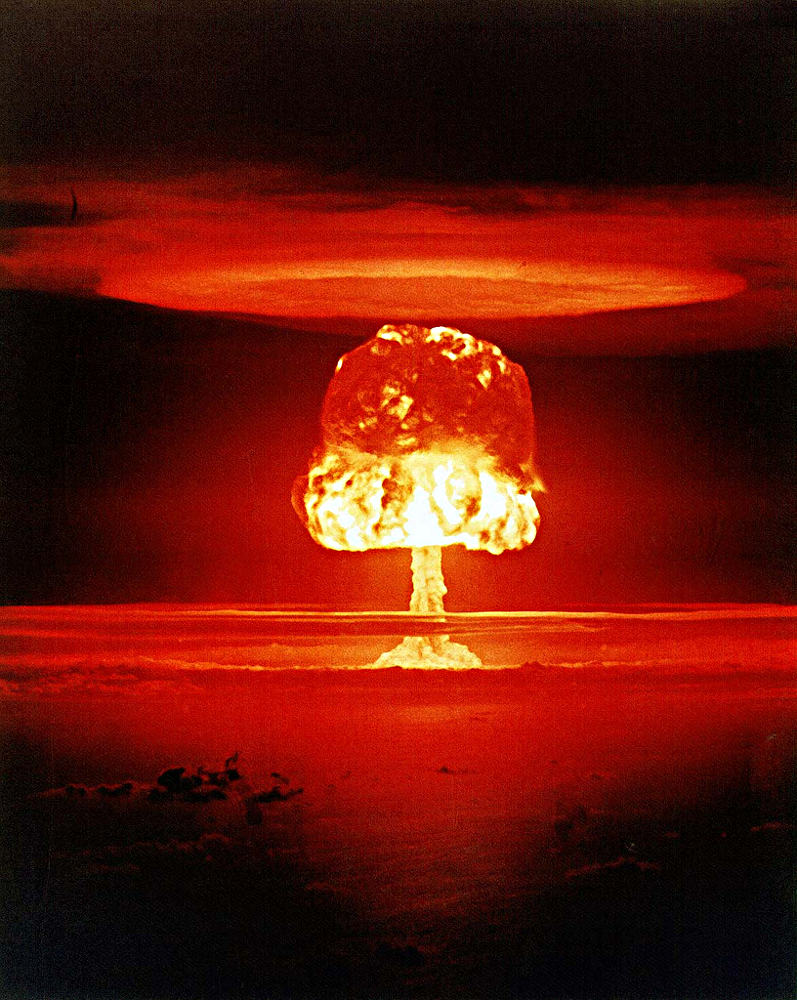

Having a yield of 11 megatons, Castle Romeo was the second US nuclear detonation and third most powerful test of the Operation Castle series. Conducted on Bikini Atoll, it was the first nuclear weapon to be tested on a barge in open water rather than a reef. It had the ability to reduce everything under 1.91 miles into ashes.
Soviet Test #123
The USSR carried out nuclear test #123 on 23 October 1961. A nuclear bomb of 12.5 megatons was used over Novaya Zemlya. A bomb of this size was able to burn everything within 2.11 square miles and leading to third-degree burns within 1,309 square miles.
Soviet Tests #158 & #168
The Soviet Union carried out nuclear tests #158 and #168 over Novaya Zemlya on 25 August and 19 September 1962 respectively. Both the detonations involved the use of 10-megaton atomic bombs. Also, these explosions had the ability to incinerate everything within 1.77 square miles of bombs’ epicenters and could cause third-degree burns up to an area of 1,090 square miles.
Soviet Tests #173, #174 & #147
The Soviet Union carried out nuclear tests #173, #174, and #147 over Novaya Zemlya from 5 August to 27 September 1962. These three nuclear tests of 20 megatons happen to be history’s 5th, 4th, and 3rd most powerful nuclear detonations. Nearly 1,000 times as strong as the Trinity bomb, a bomb of such force would burn everything within 3 square miles.
Soviet Test #219
The Soviet Union conducted nuclear test #219 over Novaya Zemlya on December 24, 1962. A bomb with a terrifying yield of 24.2 megatons would cause incineration within 3.58 square miles and produce third-degree burns within up to 2,250 square miles.
Popular Posts
What Is Trypophobia – A Disgust More Than Fear
"I can't really face small, irregularly or asymmetrically placed holes, they make me like, throw up in my mouth, cry a little bi...
Chandan Roy
16 Interesting Facts About Ambidextrous People
A lefty or left-handed uses his left hand more naturally and dominantly than the right hand. And the righty or right-handed is o...
Ethan Stephans
20 Interesting Facts About Meteoroid, Meteor and Meteorite
Watching celestial objects is a true delight. It is still fun to catch a sight of shooting stars when we grow up. A second of th...
Swati Bhandari








