Know Mountain Lion Diet, Habitat, Population & Behaviour
Mountain lion or puma is the ferocious yet cute and non-roaring mammal of the cat family. Here you will know what is its habitat distribution, behavior in social conditions, and population distribution. Also, know what the staple diet of a cougar looks like.
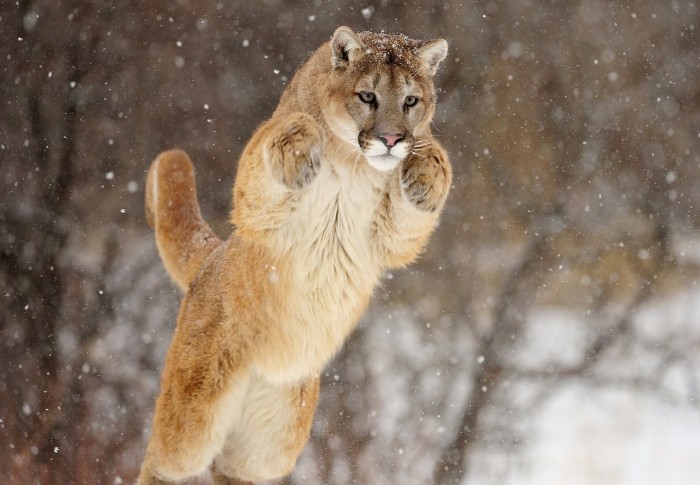

The second heaviest cat (after jaguar) in the New World, the mountain lion is found in many habitats- from southern Andes of South America to Florida swamps to Canadian Yukon forests. Mountain lion is known by not one but many names including puma, cougar, catamount, panther, and deer tiger. Interestingly, it holds Guinness record for the animal with the greatest number of names and has more than 40 names in the English language alone.
Here you’ll know about mountain lion’s diet, habitat distribution, population, and social behavior.
The Wide-Ranging Diet of the Powerful Predator ‘Cougar’

Mountain lions are successful generalist and specialist predators. From small insects to large ungulates, cougars can eat any animal and can also feed on livestock. An obligate carnivore, puma primarily needs meat for survival. They like to prey on especially deers, particularly species in North America such as elk, white-tailed deer, mule deer and even bull moose.
The other species cougars prey on include bighorn, pronghorn, porcupines, horse, Dall’s sheep, mountain goat, coyotes, fallow deer, raccoons, caribou, and even cattle and sheep. In a survey conducted in North America, it was found that 68% of prey items were ungulates, primarily deer. The Florida panther showed variation as its preference was feral hogs and armadillos.
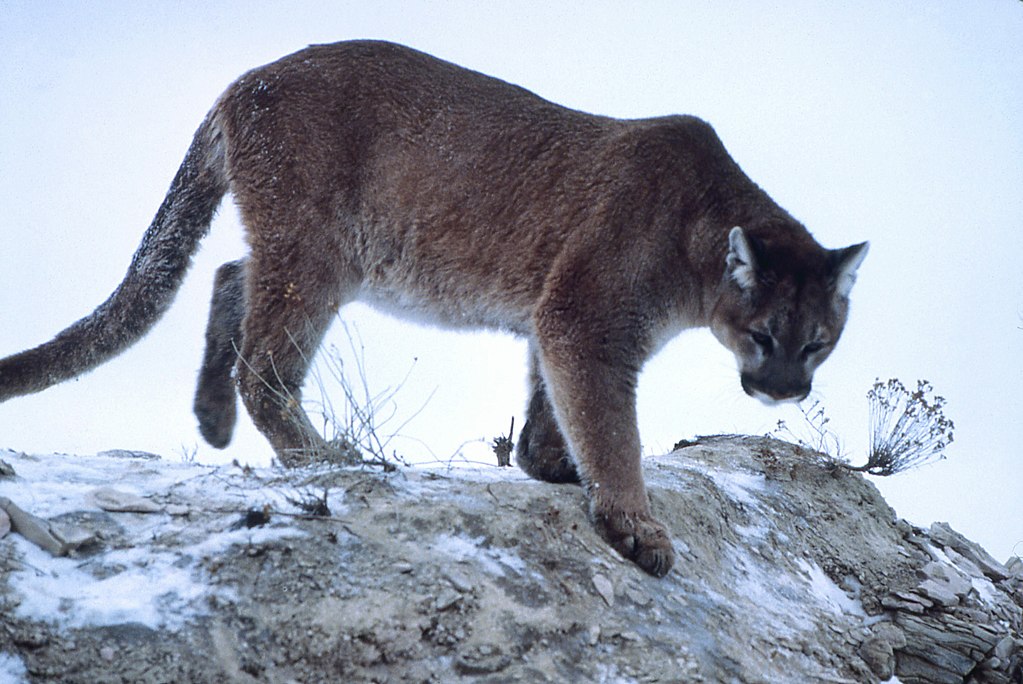

A Yellowstone National Park survey found that the panther’s chief targets were elk, followed by mule deer. The park’s gray wolves share the prey base and cougar has to face them as rival predators. A study in Alberta finds that ungulates comprised more than 99% of their diet.
In Pacific Rim National Park Reserve, the samples of droppings indicated that cougar’s diet was made up of 28% raccoons, 24% harbor seals, 24% blacktail deer, 10% North American river otters, 7% California sea lion, and 4% American mink. The rest 3% remained unidentified.

In the Central and South American cougars, there’s been a decline of deer in the diet. And rather, small to mid-sized mammals are preferred, including large rodents. The ungulates made up only 35% of preys, nearly half to that of North America. The rival larger jaguar is supposedly the reason behind the decline in the size of prey items.
Other prey species of the cougar comprise guanaco, mice, rhea, porcupines, raccoons, vicuna, hares, peccary, beavers, and wild turkey. In South America, birds and small reptiles are sometimes preyed upon but that’s a rare case in North America.
When Do They Prefer to Go on Hunting & How Do They Go About It?

Mountain lions generally hunt at night times or during dawn and dusk. And although they are skilled sprinters, they typically are ambush predators. They bring into play a blend of power and stealth, stalking their prey through bushes and trees until they find prey to lunge at. Then, they go for the back of the neck and give a deadly bite. Hiding the large carcasses, they feed on them for many days.
In every two weeks, one large ungulate is estimated to be killed. The period may dwindle for females raising young ones and it may go to one kill every 3 days when cubs are around 15 months. The mountain lion hauls its killed prey to a preferred spot, covering it with bush, and comes back to feed over a period of days.
What is Their Habitat Distribution Like?
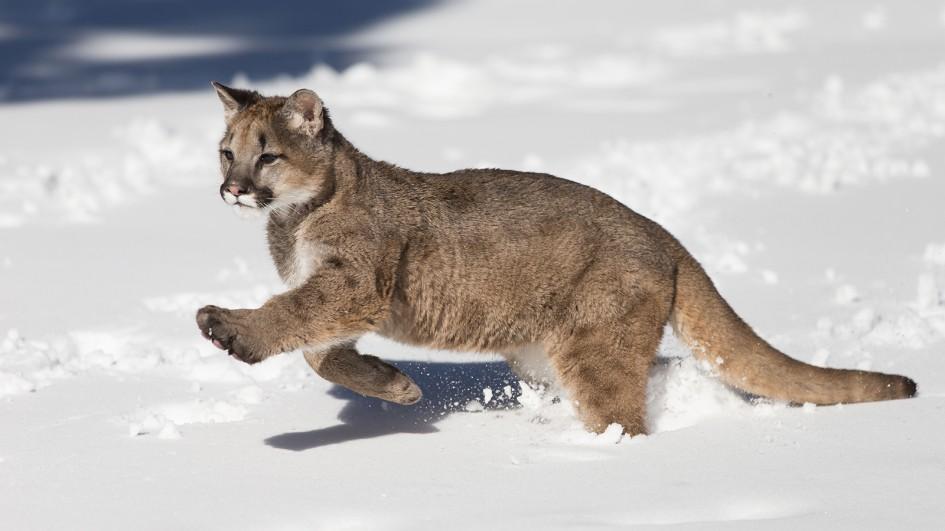

Cougars are found from Canada to Argentina, and North, Central, and South America. The largest wild cat in North America, it is the most extensively found wild land mammal in the Western Hemisphere. The puma can be spotted in most American habitat types. Six known and one unknown subspecies of cougar have been identified, most of which belong to America.
Puma’s Population Throughout the World
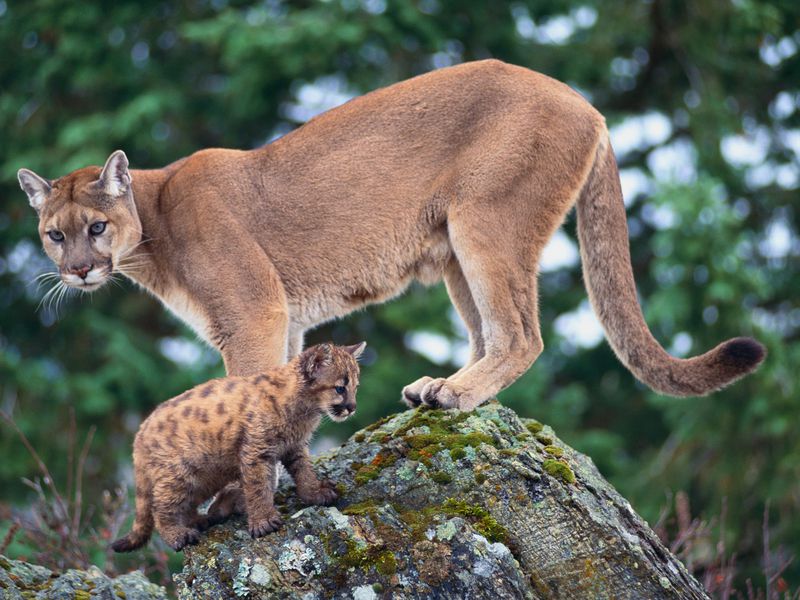

The cougar is listed as the “least concern” species (IUCN conservation status). It survives at low population densities. In the western US, nearly 30,000 cougars are there. One mountain lion subspecies, the Florida panther, is critically endangered having a population of fewer than 100 individuals.
Cougar’s Social Behavior

Shy, secretive, and solitary animals, cougars are very territorial. The mountain lions do not roar, but the female pumas have a loud scream which is believed to attract males.
Being active hunters, they may travel long distances searching for food. They require a lot of room and only a few can survive in a 30-square mile range. Solitary and shy, they are rarely seen by humans.
They seldom attack humans, usually children or solitary adults. The stats show that on average, only four attacks and one human fatality are reported every year in the whole of the US and Canada.
And good news for those who find them cute and cuddly and want to keep them as pets- they can be domesticated! They won’t even roar at you, we bet:)
Popular Posts
10 Biggest Water Dinosaurs & Sea Monsters Ever Found in Archaeology
The present-day ocean is certainly a scary place where giant sharks, whales, squids, barracuda, and numerous other marine creatures live.
Kimberly Campbell
6 Amazing Things We Should Learn From Camel Feet
Camels are a kind of mammals with the humped back, long legs, and lipped snout. They were domesticated nearly 3000 years ago are still used for transportation.
Kimberly Campbell
80 Most Popular Long Neck Dinosaurs Ever Recorded in History
Do you know the largest creatures ever walk on the earth were the long tailed and long neck dinosaurs which were called as Sauropods?
Kevin Green